Exploring ERP Systems: Cloud vs On-Premise

In the realm of enterprise resource planning (ERP), selecting the right system is pivotal for a company’s success. With various options available, understanding the distinctions between cloud-based and on-premise ERP systems is essential. In this article, we delve into the differences, compare top ERP systems, and offer insights based on industry experience.
Understanding ERP Systems
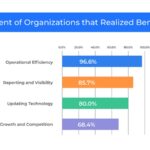
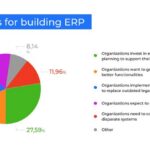
ERP systems streamline business processes and facilitate information flow within organizations. By consolidating data from multiple sources, these systems serve as a centralized repository, enhancing internal communication and efficiency. The implementation of ERP software is associated with numerous benefits, as highlighted by reports indicating high success rates among adopting companies.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
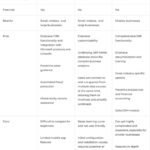
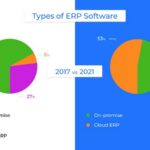
Cloud-based ERP systems are accessed via the internet, with servers hosted offsite in data centers. Typically delivered through a software as a service (SaaS) model, cloud ERPs offer scalability and accessibility, enabling remote access from any device. The popularity of cloud ERP solutions has surged in recent years due to their ease of maintenance and flexibility.
Advantages of Cloud ERP Systems
- Ease of Maintenance: Vendors handle updates, backups, and hardware maintenance, reducing the burden on internal IT teams.
- Accessibility: Users can access data from anywhere, promoting flexibility and efficiency.
- Scalability: Cloud ERPs can easily accommodate business growth by offering on-demand resources and features.
Disadvantages of Cloud ERP Systems
- Internet Dependency: Reliance on a stable internet connection may pose challenges in areas with connectivity issues.
- Limited Customization: Some cloud ERPs offer fewer customization options compared to on-premise solutions.
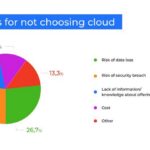
- Data Security Concerns: Companies may be apprehensive about data security in offsite cloud servers, especially in highly regulated industries.
On-Premise ERP Systems
On-premise ERP systems are installed and maintained internally, providing organizations with complete control over their infrastructure. Despite the rise of cloud solutions, on-premise deployments remain prevalent, particularly in industries prioritizing data security and customization.
Advantages of On-Premise ERP Systems
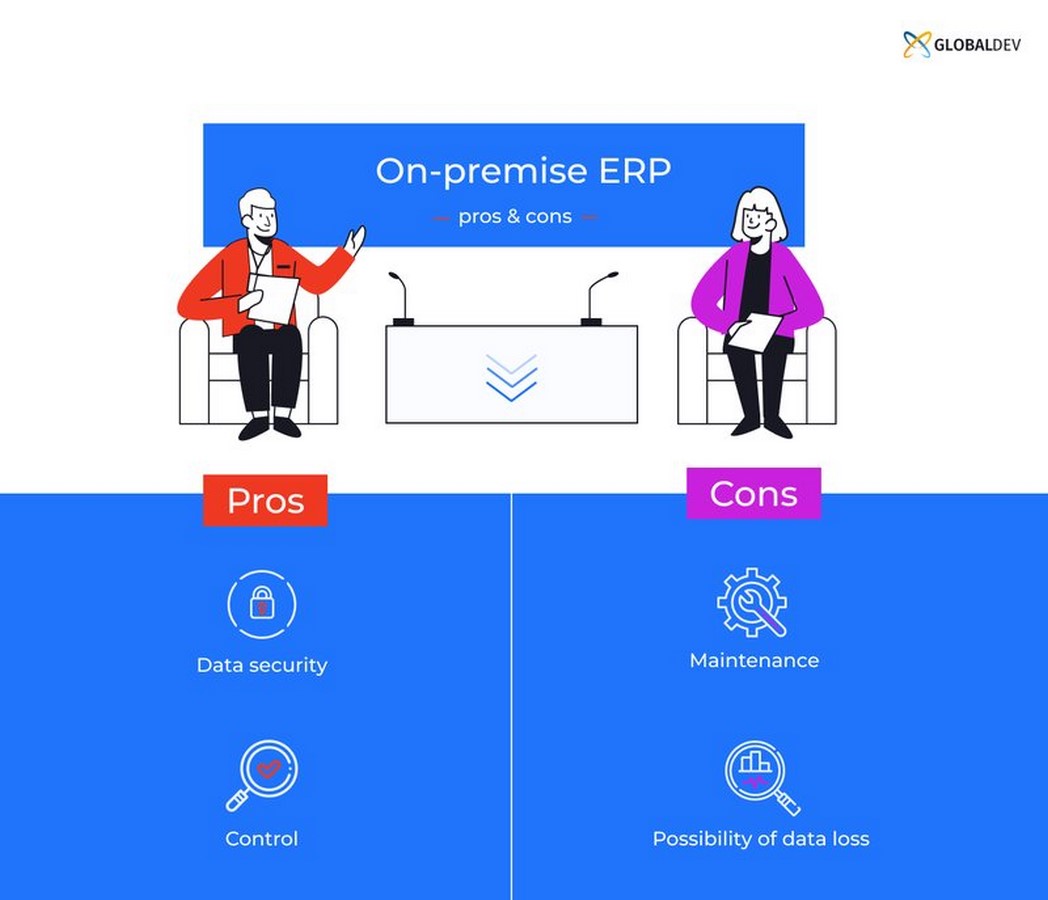
- Control and Customization: Organizations have full autonomy over system updates, security measures, and customizations.
- Data Security: Sensitive data remains on-site, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or breaches.
- No Internet Dependency: Operations are not affected by internet outages, ensuring uninterrupted access to critical systems.
Disadvantages of On-Premise ERP Systems
- Maintenance Complexity: Managing hardware and software maintenance can be resource-intensive and costly.
- Limited Accessibility: Access to data is restricted to on-site locations, potentially hindering remote work capabilities.
- Higher Upfront Costs: Initial investments in hardware and infrastructure are typically higher compared to cloud deployments.
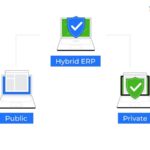
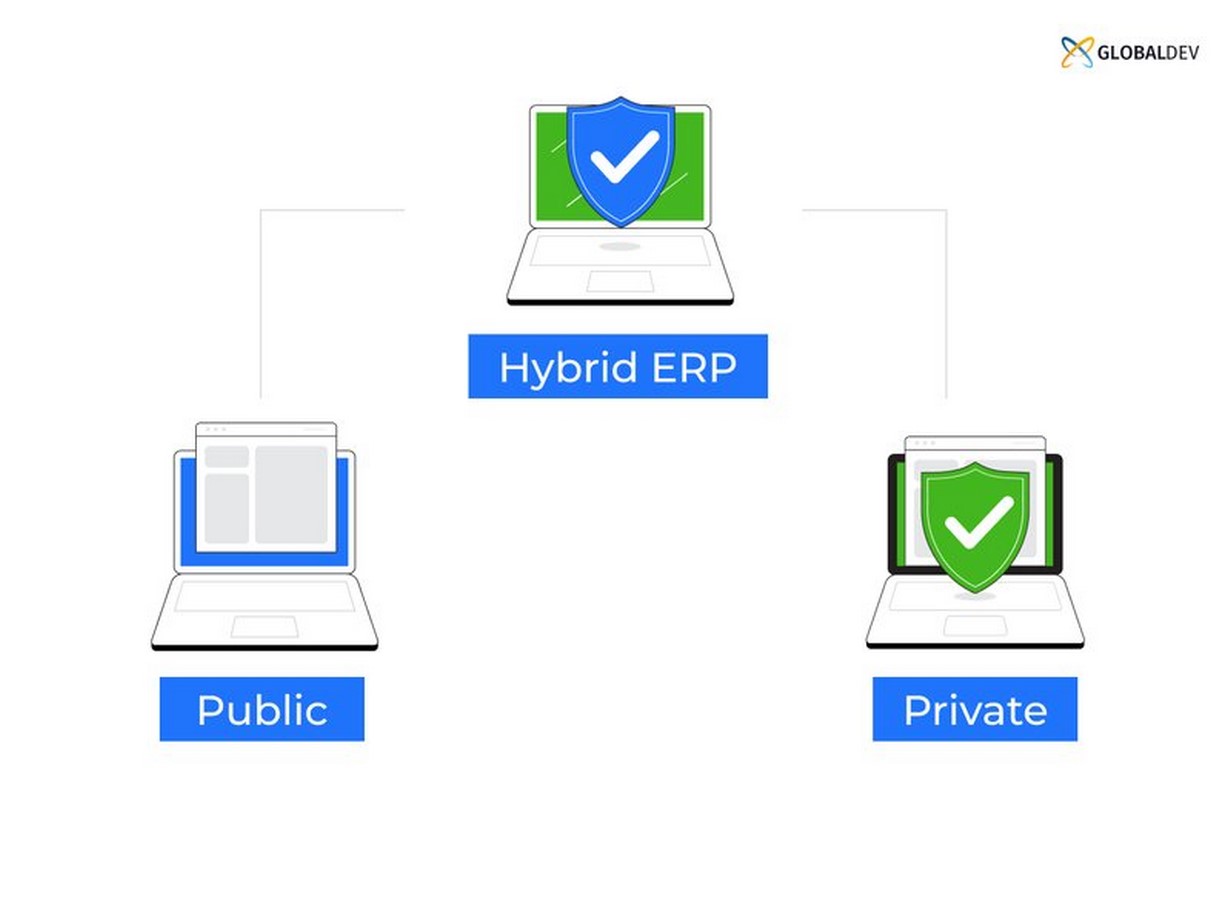
Hybrid ERP Solutions
Hybrid ERP solutions offer a middle ground, allowing organizations to retain control over critical data while leveraging cloud benefits for specific functions. By combining on-premise and cloud solutions, businesses can optimize their infrastructure according to their needs and preferences.
Choosing the Right ERP System
Selecting between cloud-based and on-premise ERP systems depends on various factors, including organizational size, industry regulations, and budget constraints. While cloud solutions offer scalability and convenience, on-premise deployments provide greater control and security. Hybrid solutions offer flexibility and customization options tailored to specific requirements.
Expert Advice from Globaldev
Based on industry experience, Globaldev recommends:
- On-Premise ERP: Suitable for midsize to large companies prioritizing data security, customization, and internal control.
- Cloud ERP: Ideal for organizations seeking scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency, with minimal IT overhead.
- Hybrid ERP: Recommended for businesses requiring a balance between control and cloud benefits, allowing for tailored solutions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right ERP system is crucial for driving business efficiency and success. Whether opting for cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid solutions, organizations must align their choice with their unique requirements and objectives. With the guidance of experienced partners like Globaldev, companies can navigate the complexities of ERP selection and implementation to achieve optimal outcomes.